Long-read transcriptome sequencing of CLL and MDS patients uncovers molecular effects of SF3B1 mutations
SF3B1 mediated splicing changes in CLL and MDS
Background
Mutations in splicing factor 3B subunit 1 (SF3B1) frequently occur in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) and myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS). These mutations have a different effect on the disease prognosis with beneficial effect in MDS and worse prognosis in CLL patients. A full-length transcriptome approach can expand our knowledge on SF3B1 mutation effects on RNA splicing and its contribution to patient survival and treatment options.
Results
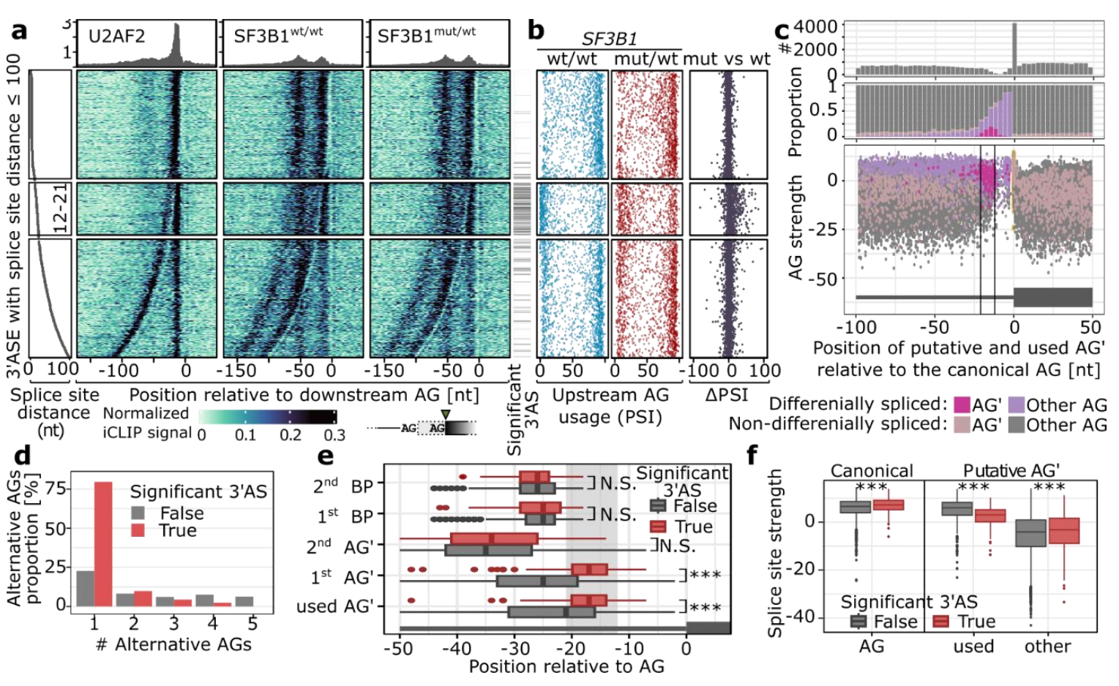
We applied long-read transcriptome sequencing to 44 MDS and CLL patients with and without SF3B1 mutations and found > 60% of novel isoforms. Splicing alterations were largely shared between cancer types and specifically affected the usage of introns and 3’ splice sites. Our data highlighted a constrained window at canonical 3’ splice sites in which dynamic splice site switches occurred in SF3B1-mutated patients. Using transcriptome-wide RNA binding maps and molecular dynamics simulations, we showed multimodal SF3B1 binding at 3’ splice sites and predicted reduced RNA binding at the second binding pocket of SF3B1K700E.
Conclusions
Our work presents the hitherto most complete long-read transcriptome sequencing study in CLL and MDS and provides a resource to study aberrant splicing in cancer. Moreover, we showed that different disease prognosis results most likely from the different cell types expanded during cancerogenesis rather than different mechanism of action of the mutated SF3B1. These results have important implications for understanding the role of SF3B1 mutations in hematological malignancies and other related diseases.
The full manuscript can be found at bioRxiv.